
Deforestation Monitoring Beyond Concessions
Spatial datasetDeforestation on the land of plantation companies and major growers has long been under the spotlight. Nonetheless, smallholders and out-growers […]
READ
Spatial Dataset
Global
Agriculture (oil palm)
Data Use Agreement
Remote Sensing, Land Use Change Analysis, Document, Field Survey
25
4429
December 2019
August 2022
Biannually (6 months)
3.59 GB
KML, XLS, SHP, GEOJSON
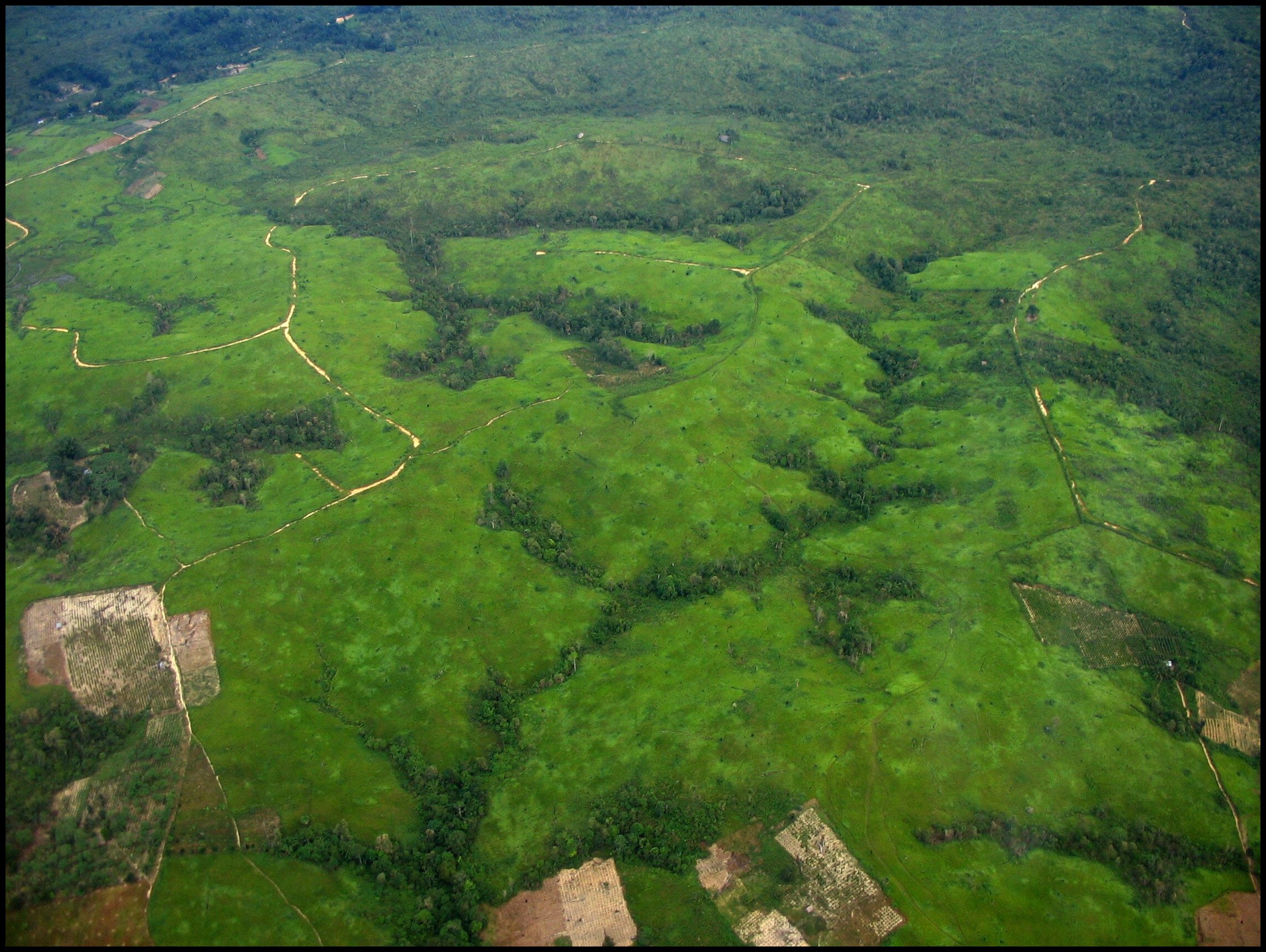
Commodity-driven deforestation and peatland loss are some of the main drivers of climate change and biodiversity loss, and are significant GHG sources. In an IPCC report published in 2022, it is estimated that agriculture, forestry and other land use contributed to 22% of the total anthropogenic CO₂ emission. In Indonesia and Malaysia alone, our research in October 2022 found that 305,143 ha of forest and 395,312 ha of peat were cleared by 296 palm plantation company groups during 2016-2021, which correspond to around 455 million tons of GHG emission.
Many businesses have benefitted from non-compliant development and illegal land clearing, and growers, millers, refiners, traders, processors and end users all share the responsibility to offset the harm caused. While businesses pledge to become net zero or carbon neutral, assessing past liability helps to assess the integrity of these commitments and hold all parties accountable.
This dataset uses satellite imagery and concession mapping to show past liability as the total loss of forests and peatland to oil palm plantations since 31st December 2015. Users can see the total amount of land cleared by individual company groups, visualize a recovery plan for implementation, and facilitate securing of social forestry rights to respective local communities.
This dataset includes: